1. Introduction to Graphite Crucible
Graphite crucible is a high-performance container crafted from advanced carbon-based materials, designed to withstand extreme temperatures and chemical environments. Used extensively in industrial melting, casting, and synthesis processes, these crucibles leverage the unique properties of graphite—such as thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and structural stability—to contain and process molten metals, alloys, and other high-temperature materials.
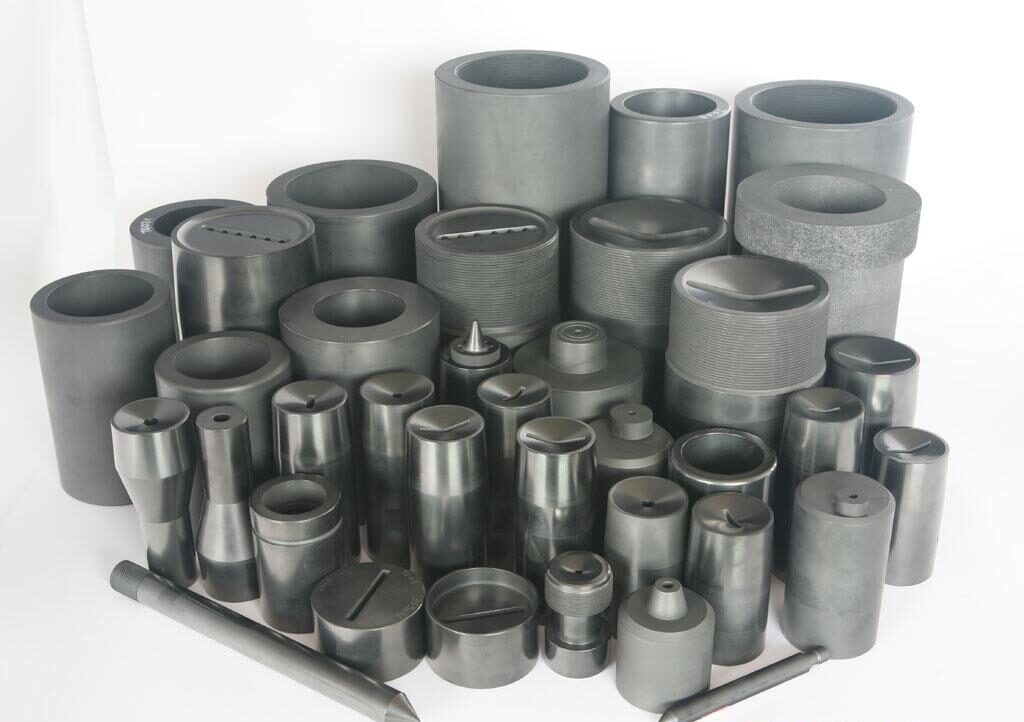

2. Material Composition and Manufacturing
2.1 Key Materials
Graphite crucibles are primarily made from:
- Natural or synthetic graphite: Providing excellent heat resistance (up to 3,000°C in inert atmospheres) and low thermal expansion.
- Binders and additives: Such as clay, silicon carbide, or resin, which enhance mechanical strength and impermeability.
2.2 Production Process
Manufacturing involves:
- Mixing raw materials into a homogeneous blend.
- Molding into desired shapes (cylindrical, rectangular, or custom forms).
- Heat-treating to optimize density and resistance to thermal shock.
3. Critical Properties of Graphite Crucible
3.1 Thermal Performance
- High melting point: Retains structural integrity in extreme heat, ideal for melting metals like aluminum, copper, and precious metals.
- Superior thermal conductivity: Ensures uniform heating and reduces energy consumption.
- Low thermal expansion: Minimizes cracking from rapid temperature changes (thermal shock resistance).
3.2 Chemical Resistance
- Inert to most molten metals, acids, and alkalis, making them suitable for reactive environments (e.g., semiconductor crystal growth).
3.3 Mechanical Strength
- Lightweight yet durable, with high compressive strength that withstands mechanical stress during handling and pouring.
4. Primary Applications Across Industries
4.1 Metal Casting & Foundries
- Melting and holding molten metals: Used in die casting, sand casting, and investment casting for automotive components, aerospace parts, and industrial machinery.
- Example: Processing aluminum alloys for engine parts requires crucibles that resist erosion from corrosive flux agents.
4.2 Semiconductor & Electronics
- Single crystal growth: Crucibles hold silicon or germanium melts during Czochralski (Cz) or Bridgman processes for semiconductor wafers.
- Purity criticality: Low ash content and minimal metal ion leaching ensure contamination-free production of microchips and LED substrates.
4.3 Renewable Energy
- Solar panel manufacturing: Processes silicon ingots for photovoltaic cells, demanding crucibles with precise thermal uniformity.
- Battery production: Handles molten salts in lithium-ion battery electrode synthesis.
4.4 Laboratory & Research
- High-temperature synthesis: Ideal for chemical reactions, catalyst testing, and material science experiments (e.g., graphene oxide production).
5. Advantages Over Alternative Crucible Materials
| Material | Graphite Crucible | Silica/Alumina Crucible | Metal Crucible |
| Temperature Limit | 3,000°C (inert) | 1,700°C | 1,200°C (depending on metal) |
| Chemical Inertness | Excellent (non-reactive with most melts) | Good (but reacts with alkali metals) | Poor (reacts with acids) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Superior (low expansion) | Moderate | Low (high thermal stress) |
| Weight-to-Strength Ratio | High (lightweight yet strong) | Moderate | Low (heavy for same size) |
6. How to Choose the Right Graphite Crucible
6.1 Key Selection Criteria
- Temperature requirements: Match the crucible’s max working temperature to your process (e.g., 1,500°C for brass vs. 2,500°C for silicon).
- Chemical compatibility: Ensure resistance to specific melts (e.g., avoid graphite for oxidizing environments without protective coatings).
- Shape & size: Customize dimensions for your furnace or casting equipment—common sizes range from 50ml lab crucibles to 5,000L industrial-scale vessels.
- Quality certifications: Look for ISO 9001:2015 compliance and material testing reports to guarantee consistency.
6.2 Coatings for Specialized Needs
- Silicon carbide (SiC) coating: Enhances oxidation resistance in air at temperatures above 700°C.
- Graphite nitride coating: Improves corrosion resistance in molten salt applications.
7. Jiaxin Graphite: Your Trusted Crucible Partner
As a leading ISO-certified manufacturer with 18+ years of expertise, Jiaxin Graphite delivers:
- Custom solutions: Tailored crucible designs for unique industrial and research requirements.
- Premium materials: Using 99.9% pure graphite and advanced composite formulations for optimal performance.
- Global reliability: Exporting to 50+ countries, with rapid turnaround for both standard and high-purity crucibles.
8. Conclusion
Graphite crucibles are indispensable in modern manufacturing, bridging high-temperature performance with chemical stability. Whether for large-scale metal casting or precision semiconductor production, their versatility and durability make them a preferred choice across industries. By understanding your process needs and partnering with a reputable supplier, you can maximize efficiency, reduce downtime, and ensure consistent quality in high-temperature operations.
9. Ready to Explore Your Crucible Solution?
Contact Jiaxin Graphite today for a free consultation on selecting the right graphite crucible for your application. Our technical team is available to discuss material specifications, customization options, and global delivery solutions—get in touch to start optimizing your processes!
- graphite mould
- graphite products
- graphite machining
- graphite plate
- graphite crucible
- graphite boat
- high purity carbon graphite
- graphite board
- graphite roller
- Graphite product
- Graphite electrode
- Graphite electrodes
- Tube graphite
- Glass graphite mold
- Graphite bearings
- Graphite moulds for glass
- Bearing graphite
- Block of graphite
- Carbon graphite bearings
- Custom graphite parts
- Graphite for sale
- Graphite material
- Graphite materials
- Graphite supplier
- Graphite suppliers
- Machine graphite
- Graphite application
- Graphite blocks for sale