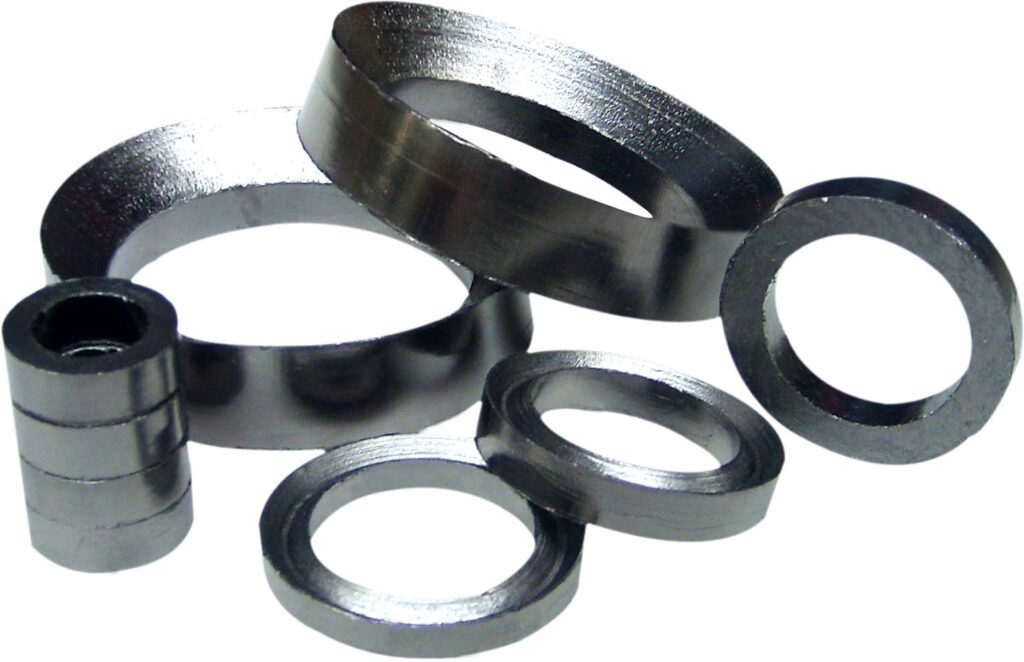
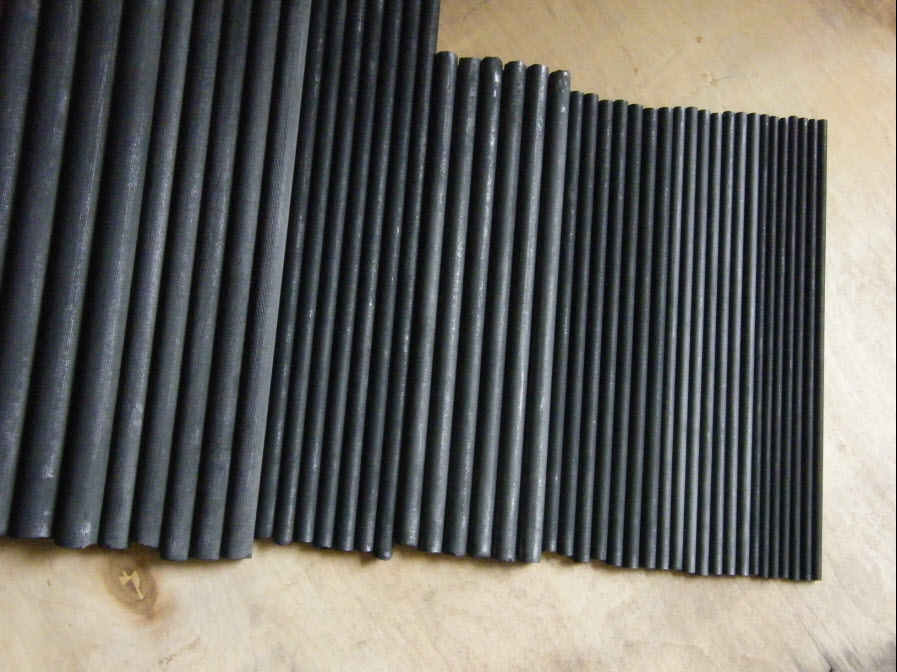
Graphite rods are cylindrical components crafted from high-purity graphite, a crystalline form of carbon known for its unique combination of electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. Widely used in industrial, energy, and technological applications, these rods leverage graphite’s natural properties to solve challenges in high-temperature, high-performance environments. This article explores what graphite rods are, their key characteristics, common types, and diverse applications.

What Are Graphite Rods?
Graphite rods are solid, cylindrical structures made from processed graphite materials—either natural graphite ore or synthetic graphite produced through carbonization and graphitization of petroleum coke. Their molecular structure, featuring layered hexagonal carbon sheets, gives them exceptional:
- Electrical conductivity (similar to metals)
- Heat resistance (stable up to 3,000°C in inert atmospheres)
- Corrosion resistance (impervious to most acids, alkalis, and molten metals)
- Self-lubricating properties (low friction due to layered structure)
These attributes make them indispensable in industries where traditional metal or ceramic materials fall short.
Key Properties of Graphite Rods
1. Exceptional Thermal Performance
Graphite rods maintain structural integrity in extreme heat, making them ideal for furnace components, thermal conductors, and mold materials in high-temperature processes. They also exhibit low thermal expansion, reducing the risk of cracking from thermal stress.
2. Superior Electrical Conductivity
As a non-metallic conductor, graphite rods conduct electricity efficiently without oxidation, making them critical in electrochemical applications like batteries, electrodes, and semiconductor manufacturing.
3. Chemical Inertness
Resistant to most corrosive substances, graphite rods excel in harsh environments, such as chemical reactors, electroplating tanks, and acid-processing equipment.
4. Lightweight & Machinable
Despite their robust performance, graphite rods are lightweight and easily machined into precise dimensions, allowing customization for unique industrial needs.
Common Types of Graphite Rods
Graphite rods are categorized by purity, structure, and application:
1. Electrode Graphite Rods
- Purity: 90–99% carbon
- Use Case: Electric arc furnaces (EAF) for steelmaking, where they generate arcs to melt scrap metal. Their high conductivity and low ash content minimize contamination.
2. High-Purity Graphite Rods
- Purity: 99.9%+ carbon (often synthetic graphite)
- Use Case: Semiconductor manufacturing (wafer production), nuclear reactors (control rods), and aerospace (thermal management systems).
3. Lubricating Graphite Rods
- Structure: Impregnated with oils or polymers for enhanced lubrication
- Use Case: Mechanical systems requiring low-friction components, such as bearings in high-temperature ovens or conveyor belts.
4. Composite Graphite Rods
- Composition: Mixed with carbon fibers or ceramics for enhanced strength
- Use Case: High-load applications like mold supports in foundries or precision instruments.
Diverse Applications of Graphite Rods
1. Industrial Manufacturing
- Steelmaking & Foundries: Electrode rods in EAFs, crucibles for melting non-ferrous metals.
- Chemical Processing: Corrosion-resistant rods in reactors, heat exchangers, and filtration systems.
2. Energy Sector
- Batteries: Anode materials in lithium-ion batteries (synthetic graphite rods for consistency).
- Nuclear Energy: Control rods to regulate neutron flow in nuclear reactors due to their neutron-absorbing properties.
3. Electronics & Semiconductors
- Chip Production: Cleanroom-compatible rods for holding silicon wafers during thermal processing.
- LED Manufacturing: Heat sinks and support structures in high-temperature deposition chambers.
4. Aerospace & Defense
- Thermal Protection: Lightweight rods for aircraft engine components and missile guidance systems.
- Satellites: Antenna parts requiring stable conductivity in extreme space temperatures.
Why Choose Graphite Rods Over Other Materials?
- Cost-Effective: Cheaper than rare metals like tungsten or molybdenum in high-temperature setups.
- Versatile: Adaptable to diverse environments—from molten metal baths to ultra-high vacuums.
- Sustainable: Graphite is a naturally abundant resource, and synthetic graphite production has lower carbon intensity than many metal alloys.
How to Select the Right Graphite Rods?
- Purity Requirements: Higher purity for sensitive applications (semiconductors, nuclear); standard purity for industrial use.
- Mechanical Properties: Consider density, hardness, and flexural strength based on load requirements.
- Environment: Evaluate temperature, chemical exposure, and electrical/thermal needs.
- Manufacturer Expertise: Partner with suppliers like Jiaxing Graphite, specializing in custom machining and material optimization for specific industries.
Conclusion
Graphite rods are a testament to nature’s engineering—combining simplicity with extraordinary performance. From powering steel mills to enabling next-gen semiconductors, their versatility makes them a cornerstone of modern industry. As technology demands higher efficiency and durability, graphite rods continue to prove their value in solving some of the world’s most challenging engineering problems.
Ready to explore how graphite rods can enhance your operations? Visit Jiaxingraphite.com to discover our range of high-quality graphite products and customized solutions.